MySQL Trigger
A trigger in MySQL is a set of SQL statements that reside in a system catalog. It is a special type of stored procedure that is invoked automatically in response to an event. Each trigger is associated with a table, which is activated on any DML statement such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.A trigger is called a special procedure because it cannot be called directly like a stored procedure. The main difference between the trigger and procedure is that a trigger is called automatically when a data modification event is made against a table. In contrast, a stored procedure must be called explicitly.
Generally, triggers are of two types according to the SQL standard:
- row-level triggers
- statement-level triggers.
Row-Level Trigger
It is a trigger, which is activated for each row by a triggering statement such as insert, update, or delete. For example, if a table has inserted, updated, or deleted multiple rows, the row trigger is fired automatically for each row affected by the insert, update, or delete statement.
Statement-Level Trigger
It is a trigger, which is fired once for each event that occurs on a table regardless of how many rows are inserted, updated, or deleted.
Difference between Row level & Statement level trigger:-
Row-level triggers execute once for each row in a transaction. Statement-level triggers execute once for each transaction. For example, if a single transaction inserted 500 rows into the Customer table, then a statement-level trigger on that table would only be executed once.Use of triggers in MySQL
We need/use triggers in MySQL due to the following features:
When we use a statement that does not use INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE query to change the data in a table, the triggers associated with the trigger will not be invoked.
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name trigger_time trigger_event
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
--variable declarations
--trigger code
END;
- Triggers help us to enforce business rules.
- Triggers help us to validate data even before they are inserted or updated.
- Triggers help us to keep a log of records like maintaining audit trails in tables.
- SQL triggers provide an alternative way to check the integrity of data.
- Triggers provide an alternative way to run the scheduled task.
- Triggers increases the performance of SQL queries because it does not need to compile each time the query is executed.
- Triggers reduce the client-side code that saves time and effort.
- Triggers help us to scale our application across different platforms.
- Triggers are easy to maintain.
Limitations of Using Triggers in MySQL
- MySQL triggers do not allow to use of all validations; they only provide extended validations. For example, we can use the NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK and FOREIGN KEY constraints for simple validations.
- Triggers are invoked and executed invisibly from the client application. Therefore, it isn't easy to troubleshoot what happens in the database layer.
- Triggers may increase the overhead of the database server.
Types of action in MySQL Triggers:-
We can define the maximum six types of actions or events in the form of triggers:- Before Insert: It is activated before the insertion of data into the table.
- After Insert: It is activated after the insertion of data into the table.
- Before Update: It is activated before the update of data in the table.
- After Update: It is activated after the update of the data in the table.
- Before Delete: It is activated before the data is removed from the table.
- After Delete: It is activated after the deletion of data from the table.
Naming Conventions
Naming conventions are the set of rules that we follow to give appropriate unique names. It saves our time to keep the work organize and understandable. Therefore, we must use a unique name for each trigger associated with a table. However, it is a good practice to have the same trigger name defined for different tables.MySQL Create Trigger
We can create a new trigger in MySQL by using the CREATE TRIGGER statement. It is to ensure that we have trigger privileges while using the CREATE TRIGGER command. The following is the basic syntax to create a trigger:CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name trigger_time trigger_event
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
--variable declarations
--trigger code
END;
Parameter Explanation:-
The create trigger syntax contains the following parameters:
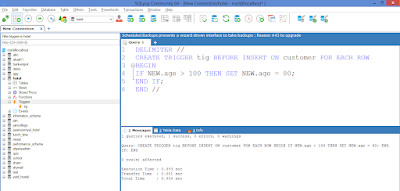
CREATE TRIGGER tig BEFORE INSERT ON customer FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.age > 100 THEN SET NEW.age = 80;
END IF;
END //
- trigger_name: It is the name of the trigger that we want to create. It must be written after the CREATE TRIGGER STATEMENT. It is to make sure that the trigger name should be unique within the schema.
- trigger_time: It is the trigger action time, which should be either BEFORE or AFTER. It is the required parameter while defining a trigger. It indicates that the trigger will be invoked before or after each row modification occurs on the table.
- trigger_event: It is the type of operation name that activates the trigger. It can be either INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operation. The trigger can invoke only one event at one time. If we want to define a trigger which is invoked by multiple events, it is required to define multiple triggers, and one for each event.
- table_name: It is the name of the table to which the trigger is associated. It must be written after the ON keyword. If we did not specify the table name, a trigger would not exist.
- BEGIN END Block: Finally, we will specify the statement for execution when the trigger is activated. If we want to execute multiple statements, we will use the BEGIN END block that contains a set of queries to define the logic for the trigger.
Example:-
DELIMITER //CREATE TRIGGER tig BEFORE INSERT ON customer FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.age > 100 THEN SET NEW.age = 80;
END IF;
END //


0 Comments
if u have any doubts please let me know,