SQL- DDL, DML, DCL, DTL, DQL- SQL Commands With Examples
SQL, Structured Query Language, is a programming language designed to manage data stored in relational databases.SQL Commands:-
SQL commands are instructions. It is used to communicate with the database.Types of SQL Commands:-
Data Definition Language (DDL):-
DDL changes the structure of the table like creating a table, deleting a table, altering a table, etc.
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DROP
- TRUNCATE
CREATE:-
This statement is used to create a table or a database.
‘CREATE DATABASE’ Statement:- this statement is used to create a database.
Syntax:-
CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName;
Example:-
CREATE DATABASE School;
‘CREATE TABLE’ Statement:-This statement is used to create a table.
Syntax:-
CREATE TABLE TableName (
Column1 datatype,Column2 datatype,
....
ColumnN datatype
);
Example:-
CREATE TABLE Teacher_Info(
Tid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
Tname VARCHAR(255),
Tmob VARCHAR(255),
Address VARCHAR(255),
City VARCHAR(255),
Country VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY(Tid)
);
‘CREATE DATABASE’ Statement:- this statement is used to create a database.
Syntax:-
CREATE DATABASE DatabaseName;
Example:-
CREATE DATABASE School;
‘CREATE TABLE’ Statement:-This statement is used to create a table.
Syntax:-
CREATE TABLE TableName (
Column1 datatype,Column2 datatype,
....
ColumnN datatype
);
Example:-
CREATE TABLE Teacher_Info(
Tid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
Tname VARCHAR(255),
Tmob VARCHAR(255),
Address VARCHAR(255),
City VARCHAR(255),
Country VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY(Tid)
);
DROP:-
This statement is used to drop an existing table or a database. It is used to delete both the structure and record stored in the table or a database.
‘DROP DATABASE’ Statement:-This statement is used to drop an existing database.
Syntax:-
DROP DATABASE DatabaseName;
Example:-
DROP DATABASE School;
‘DROP TABLE’ Statement:-This statement is used to drop an existing table.
Syntax:-
DROP TABLE TableName;
Example:-
DROP Table Teacher_Info;
‘DROP DATABASE’ Statement:-This statement is used to drop an existing database.
Syntax:-
DROP DATABASE DatabaseName;
Example:-
DROP DATABASE School;
‘DROP TABLE’ Statement:-This statement is used to drop an existing table.
Syntax:-
DROP TABLE TableName;
Example:-
DROP Table Teacher_Info;
TRUNCATE:-
It is used to delete all the rows from the table and free the space containing the table( it also deleted the index file of that table).
Syntax:-
TRUNCATE TABLE TableName;
Example:-
TRUNCATE Table Teacher_Info;
Syntax:-
TRUNCATE TABLE TableName;
Example:-
TRUNCATE Table Teacher_Info;
ALTER:-
This command is used to delete, modify or add constraints or columns in an existing table.
ADD/DROP COLUMN:-we can use the ALTER TABLE statement with ADD/DROP Column command according to our need.
Syntax:-
ALTER TABLE TableName ADD ColumnName Datatype;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info ADD Salary varchar(255);
Syntax:-
ADD/DROP COLUMN:-we can use the ALTER TABLE statement with ADD/DROP Column command according to our need.
Syntax:-
ALTER TABLE TableName ADD ColumnName Datatype;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info ADD Salary varchar(255);
Syntax:-
ALTER TABLE TableName DROP COLUMN ColumnName;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info DROP COLUMN Salary ;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info DROP COLUMN Salary ;
ALTER TABLE Statement with ALTER COLUMN:-This statement is used to change the data type of an existing column in a table.
Syntax:-
ALTER TABLE TableName MODIFY COLUMN ColumnName Datatype;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info MODIFY COLUMN salary INT;
Syntax:-
ALTER TABLE TableName MODIFY COLUMN ColumnName Datatype;
Example:-
ALTER TABLE Teacher_Info MODIFY COLUMN salary INT;
Data Manipulation Language:-
DML commands are used to modify the database. It is responsible for all form of changes in the database. commands that come under DML are:-
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
INSERT:-
This statement is used to insert new records into the table.
Syntax:-
INSERT INTO TableName (Column1, Column2, Column3, ...,ColumnN) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
OR
INSERT INTO TableName VALUES (Value1, Value2, Value3, ...);
Example:-
INSERT INTO Teacher_Info(TID, TName, Tmob, Address, City, Country) VALUES ('06', 'Sanjana','9921321141', 'House No 12', 'Chennai', 'India');
Example 2:-
INSERT INTO Teacher_Info VALUES ('07', 'Sayantini', '9934567654', 'RingRoad 21', 'Delhi', 'India');
Syntax:-
INSERT INTO TableName (Column1, Column2, Column3, ...,ColumnN) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
OR
INSERT INTO TableName VALUES (Value1, Value2, Value3, ...);
Example:-
INSERT INTO Teacher_Info(TID, TName, Tmob, Address, City, Country) VALUES ('06', 'Sanjana','9921321141', 'House No 12', 'Chennai', 'India');
Example 2:-
INSERT INTO Teacher_Info VALUES ('07', 'Sayantini', '9934567654', 'RingRoad 21', 'Delhi', 'India');
UPDATE:-
This command is used to update or modify the value of a column in the table.
Syntax:-
UPDATE TableName SET Column1 = Value1, Column2 = Value2, ... WHERE Condition;
Example:-
UPDATE Teacher_Info SET Tname = 'Aahana', City= 'Ahmedabad' WHERE TID = 1;
Syntax:-
UPDATE TableName SET Column1 = Value1, Column2 = Value2, ... WHERE Condition;
Example:-
UPDATE Teacher_Info SET Tname = 'Aahana', City= 'Ahmedabad' WHERE TID = 1;
DELETE:-
It is used to remove one or more row from a table.
Syntax:-
DELETE FROM TableName WHERE Condition;
Example:-
DELETE FROM Teacher_Info WHERE Tid=1;
Syntax:-
DELETE FROM TableName WHERE Condition;
Example:-
DELETE FROM Teacher_Info WHERE Tid=1;
Data Control Language:-
DCL commands are used to grant and take back authority from any database user. Commands that come under DCL are:
- Grant
- Revoke
Grant:-
It is used to give user access Privileges to a database.
Syntax:-
GRANT PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
TO {UserName |PUBLIC };
Syntax:-
GRANT PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
TO {UserName |PUBLIC };
Here,
GRANT SELECT ON Teacher_Info TO user1;
- PrivilegeName –access granted to the user.
- ObjectName – Name of a database object like TABLE.
- UserName – Name of the user who is given the access.
- PUBLIC – To grant access rights to all users.
GRANT SELECT ON Teacher_Info TO user1;
Revoke:-
It is used to take back permissions from the user. This command is used to withdraw the user’s access privileges given by using the GRANT command.
Syntax:-
REVOKE PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
FROM {UserName |PUBLIC }
Example:-
REVOKE SELECT ON Teacher_info FROM rahul;
Syntax:-
REVOKE PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
FROM {UserName |PUBLIC }
Example:-
REVOKE SELECT ON Teacher_info FROM rahul;
Transaction Control Language:-
TCL commands can only use with DML commands like INSERT, DELETE and UPDATE only. commands that come under TCL are:
- COMMIT
- ROLLBACK
- SAVEPOINT
Commit:-
Commit command is used to save all the transactions to the database.
Syntax:-
COMMIT;
Example:-
DELETE FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE AGE = 25;
COMMIT;
Syntax:-
COMMIT;
Example:-
DELETE FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE AGE = 25;
COMMIT;
Rollback:-
Rollback command is used to undo transactions that have not already been saved to the database.
Syntax:-
ROLLBACK;
Example:-
DELETE FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE AGE = 25;
ROLLBACK;
Syntax:-
ROLLBACK;
Example:-
DELETE FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE AGE = 25;
ROLLBACK;
SAVEPOINT:-
It is used to roll the transaction back to a certain point without rolling back the entire transaction.
Syntax:-
SAVEPOINT SAVEPOINT_NAME;
Example:-
START TRANSACTION;
Syntax:-
SAVEPOINT SAVEPOINT_NAME;
Example:-
START TRANSACTION;
INSERT INTO Emp_info VALUES(05, 'Avinash');
COMMIT;
SAVEPOINT S1;
INSERT INTO Emp_info VALUES(06, 'Sanjana');
SAVEPOINT S2;
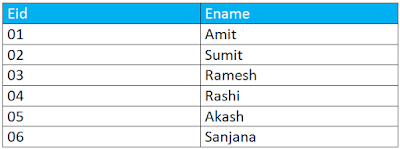
SELECT * FROM Emp_info;
The output to the above set of queries would be as follows:
Now, if we rollback to S1 using the below queries, the output is mentioned in the below table.
ROLLBACK TO S1;
SELECT * FROM Employee_Table;
COMMIT;
SAVEPOINT S1;
INSERT INTO Emp_info VALUES(06, 'Sanjana');
SAVEPOINT S2;
SELECT * FROM Emp_info;
The output to the above set of queries would be as follows:
Now, if we rollback to S1 using the below queries, the output is mentioned in the below table.
ROLLBACK TO S1;
SELECT * FROM Employee_Table;
Data Query Language:-
DQL is used to fetch the data from the database.
SELECT:-
This statement is used to select data from a database and the data returned is stored in a result table, called the result-set.
Syntax:-
SELECT Column1, Column2, ...ColumN FROM TableName;
Example:-
SELECT Tid, Tname FROM Teacher_Info;
Syntax:-
SELECT Column1, Column2, ...ColumN FROM TableName;
Example:-
SELECT Tid, Tname FROM Teacher_Info;
Related Other Post
keywords Used with the SELECT statement:
- DISTINCT
- ORDER BY
- GROUP BY
- HAVING Clause
- IN
DISTINCT:-
This statement is used to return only different values.
Example:-
SELECT DISTINCT Tname FROM Teacher_Info;
Example:-
SELECT DISTINCT Tname FROM Teacher_Info;
ORDER BY:-
The ‘ORDER BY’ statement is used to sort the required results in ascending or descending order. The results are sorted in ascending order by default.
Example:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_Info ORDER BY Tname;
Example 2:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_Info ORDER BY Tname DESC;
Example:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_Info ORDER BY Tname;
Example 2:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_Info ORDER BY Tname DESC;
GROUP BY:-
statement is used with the aggregate functions to group the result-set by one or more columns.
Example:-
SELECT COUNT(Tid), City FROM Teacher_Info GROUP BY City;
Example:-
SELECT COUNT(Tid), City FROM Teacher_Info GROUP BY City;
HAVING Clause:-
The ‘HAVING’ clause is used in SQL because the WHERE keyword cannot be used everywhere.
Example:- To list the number of Teacher in each city. The Teacher should be sorted high to low and only those cities must be included who have more than 5 Teachers
SELECT COUNT(Tid), City FROM Teacher_Info GROUP BY City HAVING COUNT(Tid) > 5 ORDER BY COUNT(Tid) DESC;
Example:- To list the number of Teacher in each city. The Teacher should be sorted high to low and only those cities must be included who have more than 5 Teachers
SELECT COUNT(Tid), City FROM Teacher_Info GROUP BY City HAVING COUNT(Tid) > 5 ORDER BY COUNT(Tid) DESC;
IN Statement:-
This statement is used to copy data from one table to another.
Example:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_info WHERE tname IN ('shyam', 'sanjana');
Example:-
SELECT * FROM Teacher_info WHERE tname IN ('shyam', 'sanjana');





0 Comments
if u have any doubts please let me know,